
Elevator safety is not just an engineering requirement—it is a daily concern for millions of passengers who rely on vertical transportation in office towers, residential complexes, hospitals, and shopping centers. One of the most overlooked yet critical components ensuring this safety is the elevator guide rail. Without durable and precisely installed guide rails, elevators risk misalignment, vibrations, or even catastrophic safety failures. For building owners, contractors, and facility managers, understanding elevator guide rails is essential to prevent costly breakdowns, minimize downtime, and protect human lives.
An elevator guide rail is a vertical steel or aluminum track installed inside the elevator shaft. Acting much like a railway track, it provides a secure and stable path for the elevator car and counterweight. The elevator car is fitted with guide shoes or roller guides that glide along these rails, ensuring smooth and aligned vertical travel.
Key roles of elevator guide rails include:
In short, guide rails are the backbone of a safe and reliable elevator system.
Guide rails operate through a direct mechanical interface with the elevator car and counterweight:
Beyond stability, guide rails play multiple roles that directly impact safety and operational reliability:
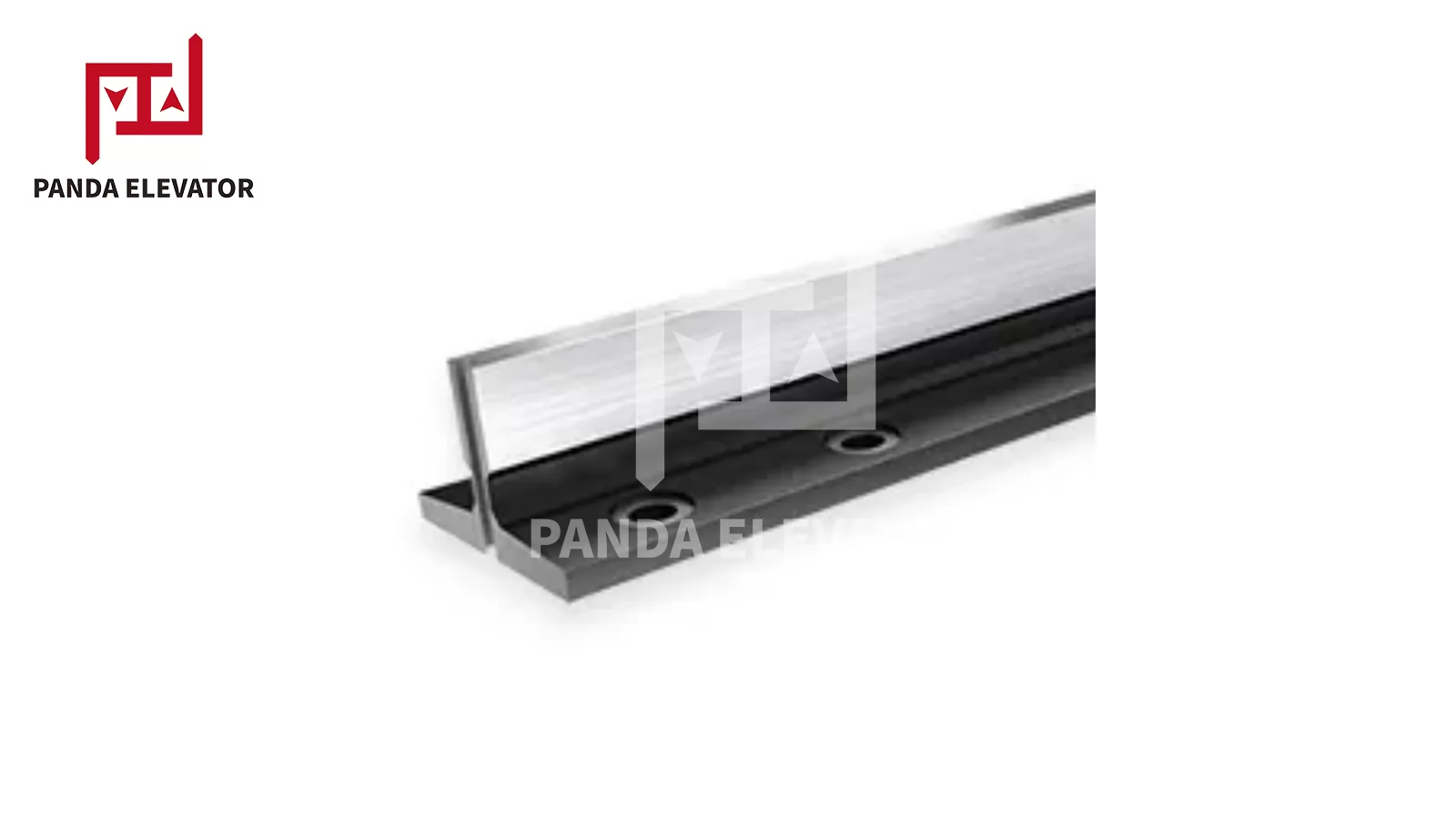

Elevator guide rails can be categorized based on their structure, function, and application. The most common classifications include:
While the classification of elevator guide rails helps us understand their structural differences and functional applications, engineers and procurement specialists often need more precise technical data to make informed decisions. This is where standardized specifications and dimensions become critical. International standards such as EN 81 and ISO/DIS 7465 define guide rail sizes, straightness, and tolerances, ensuring safety and interchangeability across different elevator systems. Below, we present the commonly used models and specifications of elevator guide rails for reference.
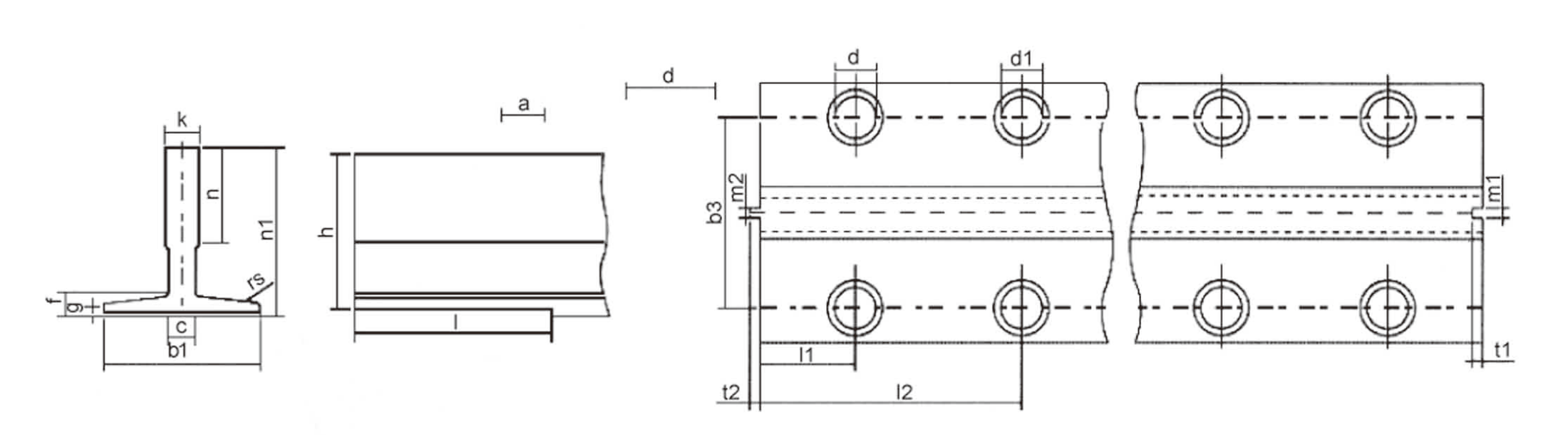
| Type | b1 | h1 | h | k | n | c | g | f | rs | m1 | m2 | t1 | t2 | l | l1 | L2 | b3 | d | d1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | |||||||||||||||||||
| ±1.5 | ±0.75 | ±0.1 |
+0.1 0 |
+3 0 |
±0.75 |
+0.06 0 |
0 -0.06 |
±0.1 | ±0.1 |
+3 0 |
±0.2 | ±0.2 | ±0.2 | ||||||
| T70-1/B | 70 | 65 | 64 | 9 | 34 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 1.5 | 3 | 2.95 | 3.5 | 3 | 128 | 25 | 105 | 42 | 13 | 13 |
| T82/B | 82.5 | 68.25 | 66.6 | 9 | 25.4 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 8.25 | 3 | 3 | 2.95 | 3.5 | 3 | 111 | 27 | 81 | 50.8 | 13 | 26 |
| T75-3/B | 75 | 62 | 61 | 10 | 30 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 2.95 | 3.5 | 3 | 123 | 30 | 90 | 43 | 13 | 26 |
| T78/B | 78 | 56 | 55 | 10 | 25 | 8 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 3 | 3 | 2.95 | 3.5 | 3 | 163 | 38 | 90 | 50 | 14 | 28 |
| T89/B | 89 | 62 | 61 | 15.88 | 33.4 | 10 | 7.9 | 11.1 | 3 | 6.4 | 6.37 | 7.14 | 6.35 | 156 | 38.1 | 114.3 | 57.2 | 13 | 26 |
| T90/B | 90 | 75 | 74 | 16 | 42 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 4 | 6.4 | 6.37 | 7.14 | 6.35 | 156 | 38.1 | 114.3 | 57.2 | 13 | 26 |
| T114/B | 114 | 89 | 88 | 16 | 38 | 10 | 8 | 12 | 4 | 6.4 | 6.37 | 7.14 | 6.35 | 156 | 38.1 | 114.3 | 74 | 17 | 33 |
| T127-1/B | 127 | 88.9 | 88 | 15.88 | 44.5 | 10 | 7.9 | 11.1 | 4 | 6.4 | 6.37 | 7.14 | 6.35 | 156 | 38.1 | 114.3 | 79.4 | 17 | 33 |
| T127-2/B | 127 | 88.9 | 88 | 15.88 | 50.8 | 10 | 12.7 | 15.9 | 5 | 6.4 | 6.37 | 7.14 | 6.35 | 156 | 38.1 | 114.3 | 79.4 | 17 | 33 |
| T140-1/B | 140 | 108 | 107 | 19 | 50.8 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 15.9 | 5 | 6.4 | 6.37 | 7.14 | 6.35 | 193 | 31.8 | 152.4 | 92.1 | 21 | 40 |
| T140-2/B | 140 | 102 | 101 | 28.6 | 50.8 | 17.5 | 14.5 | 17.5 | 5 | 6.4 | 6.37 | 7.14 | 6.35 | 193 | 31.8 | 152.4 | 92.1 | 21 | 40 |
| T140-3/B | 140 | 127 | 126 | 31.75 | 57.2 | 19 | 17.5 | 25.4 | 5 | 6.4 | 6.37 | 7.14 | 6.35 | 193 | 31.8 | 152.4 | 92.1 | 21 | 40 |
The number of guide rails required depends on the lifting height and pit depth. A common formula is:
Number of guide rails = [(Lift Height + Pit Depth) × 2] ÷ Standard Rail Length
For example, with a lift height of 3000 mm and a pit depth of 500 mm, approximately 14–15 rails are needed. This ensures proper installation and redundancy, as safety codes often require additional rails beyond the calculated minimum.
Installation of guide rails is one of the most critical phases of elevator assembly. A misaligned rail—even by a few millimeters—can lead to excessive wear, noise, or failure of safety systems.
Steps in installation include:
Only trained specialists should perform guide rail installation to meet international standards and minimize risk.
Just like any mechanical component, guide rails require regular inspection and servicing:
Neglecting maintenance can lead to increased downtime, costly replacements, and compromised passenger safety.
At Panda Elevator, we recognize that the strength of an elevator system depends on the integrity of its guide rails. That is why we offer:
By choosing Panda Elevator, building owners and contractors gain not only durable guide rails but also a long-term safety assurance backed by professional expertise.
Elevator guide rails are more than just supporting components—they are the foundation of safe, smooth, and reliable vertical transportation. From maintaining alignment to enabling emergency stops, guide rails directly affect passenger safety, comfort, and operational efficiency.
For property managers, engineers, and builders, understanding the role of elevator guide rails is crucial. And for those seeking top-tier reliability and customization, Panda Elevator provides solutions that meet global standards while ensuring every ride is secure and comfortable.