_1766114621_WNo_1600d900.webp)
Traction elevators are the most widely used elevator systems in modern buildings, particularly in mid-rise and high-rise applications. Among them, geared and gearless traction elevators represent two distinct drive technologies, each offering different performance characteristics, cost structures, and maintenance requirements.
Understanding the differences between geared and gearless traction elevators is essential for elevator manufacturers, project engineers, maintenance companies, and component buyers. This guide provides a detailed technical comparison of both systems, explains their core components, and offers practical guidance on selecting the right traction solution based on building type and operational needs. It also highlights key traction system components commonly required for installation, modernization, and long-term maintenance.
A traction elevator is a type of vertical transportation system that moves passengers or goods using a hoisting mechanism driven by ropes or belts over a traction sheave connected to an electric motor. Unlike hydraulic elevators, which rely on fluid pressure to lift the cab, traction elevators use a counterweight system to balance the weight of the elevator car, resulting in higher energy efficiency and smoother operation.
Traction elevators are classified based on the type of drive mechanism: geared traction elevators and gearless traction elevators. Both types share the core components, including a traction motor, traction sheave, ropes, counterweight, and braking system, but differ significantly in how power is transmitted and how they perform in various building applications. Understanding these differences is essential for engineers, maintenance teams, and parts buyers to make informed decisions regarding system selection and component procurement.
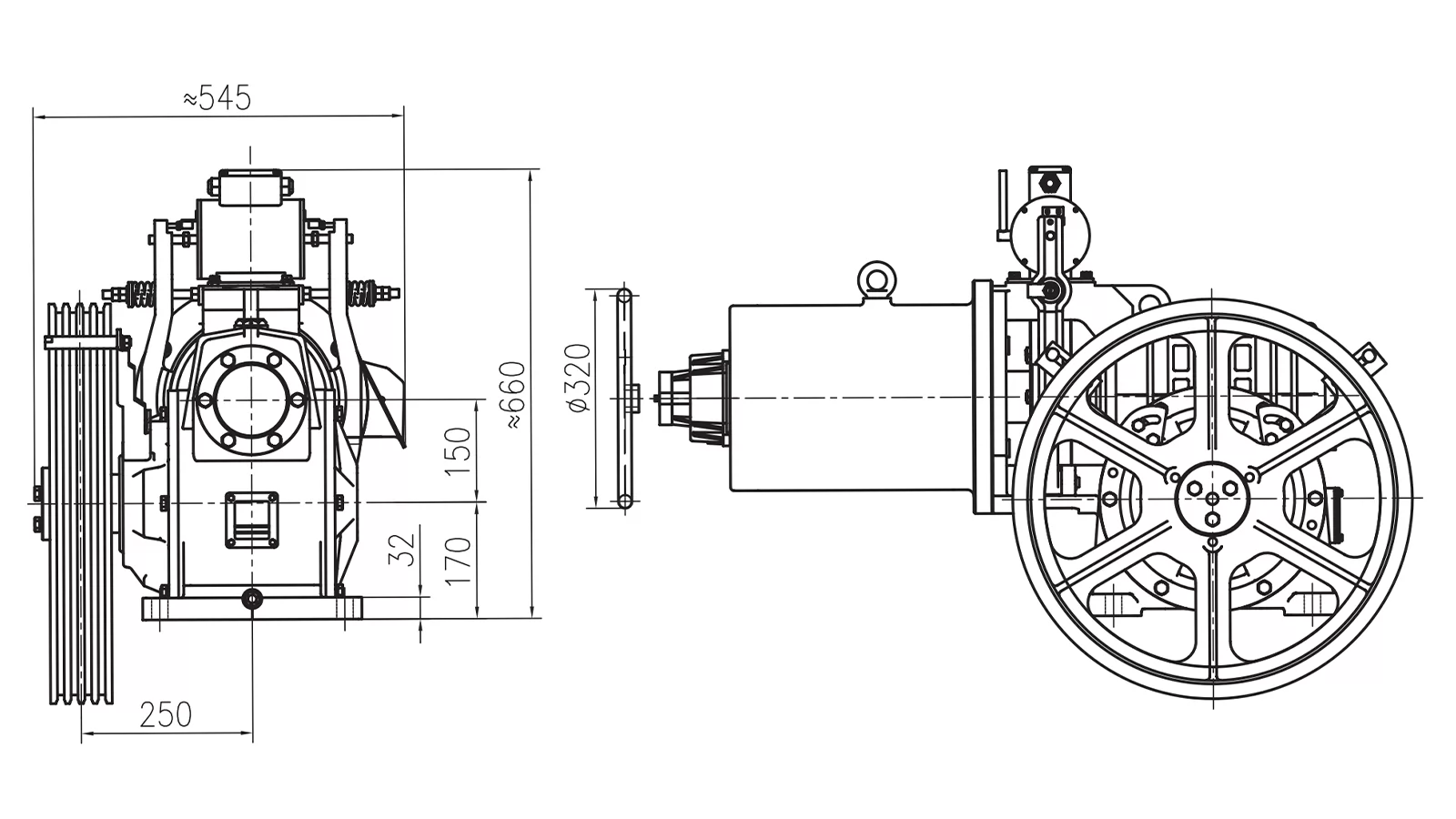
A geared traction elevator uses an electric motor connected to a gearbox to drive the traction sheave, which moves the elevator cab via steel ropes. The gearbox reduces the motor's speed while increasing torque, allowing the elevator to operate efficiently at lower speeds and mid-rise building heights. This system has been widely used for decades due to its reliability and relatively low initial cost.
In a geared traction system, the motor rotates a gearbox that, in turn, drives the traction sheave. The sheave grips the hoisting ropes connected to the elevator car and counterweight, producing smooth vertical movement. The gearbox allows precise speed control and can accommodate different load requirements.
Geared traction elevators are commonly installed in residential mid-rise buildings, hotels, and commercial offices where moderate speed and cost-efficiency are priorities.
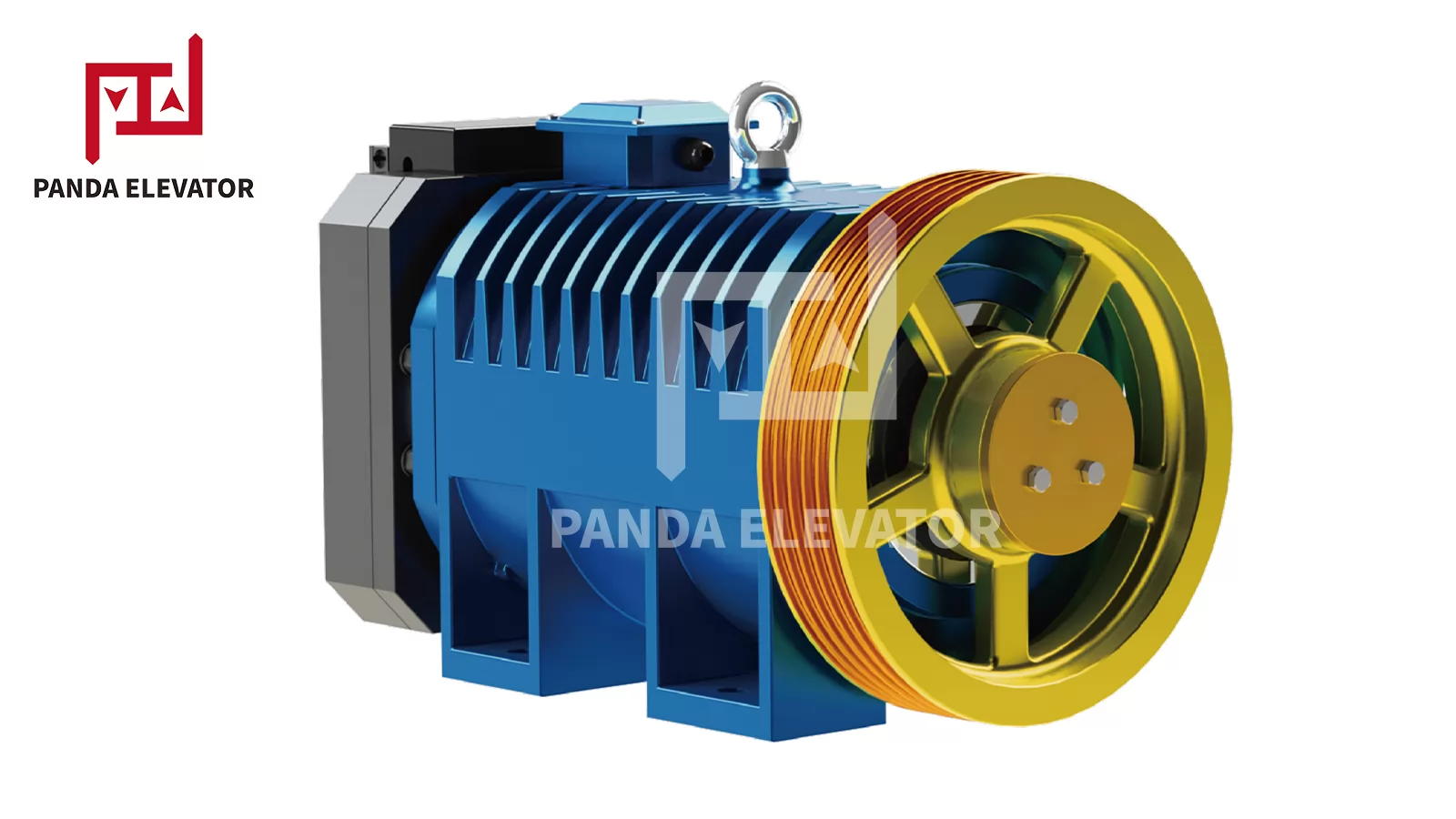

A gearless traction elevator eliminates the gearbox entirely by connecting the traction motor directly to the traction sheave. This design allows for higher speeds, smoother ride quality, and reduced mechanical losses. Gearless traction elevators are typically used in high-rise buildings where performance, energy efficiency, and passenger comfort are critical.
In a gearless system, the motor rotor is directly coupled to the traction sheave, which moves the elevator cab via steel ropes and a counterweight. This direct drive reduces mechanical complexity, eliminates the wear associated with gearboxes, and allows for precise speed control, including high-speed operation for skyscrapers.
Gearless traction elevators are ideal for high-rise commercial towers, luxury residential skyscrapers, airports, and other buildings where speed, comfort, and energy efficiency are prioritized.
While both geared and gearless traction elevators share the basic principle of using ropes, sheaves, and counterweights to move the elevator cab, the differences in drive mechanism result in distinct performance characteristics, maintenance requirements, and suitability for various building types. The table below provides a side-by-side comparison to help engineers and decision-makers evaluate which system is best suited for their project.
| Feature | Geared Traction Elevator | Gearless Traction Elevator |
|---|---|---|
| Drive Mechanism | Electric motor with gearbox | Direct drive motor (no gearbox) |
| Typical Speed | 0.5–2.5 m/s | Up to 4 m/s or more |
| Building Height Suitability | Low to mid-rise | Mid to high-rise |
| Maintenance | Requires regular gearbox servicing | Lower maintenance due to fewer mechanical parts |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | High, especially with regenerative drives |
| Noise Level | Higher due to gearbox | Low, smoother operation |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
This comparison clearly shows that geared elevators remain a cost-effective solution for moderate-rise buildings, while gearless systems are preferred for high-speed, high-rise applications where performance and energy efficiency are paramount.
Understanding the essential components of traction elevators is critical for system selection, maintenance planning, and sourcing high-quality replacement parts. Both geared and gearless traction elevators share core components, although some elements differ in design and specification.
The traction motor provides the driving force for the elevator system. In geared elevators, the motor is connected to a gearbox that adjusts speed and torque, while in gearless elevators, the motor is directly coupled to the traction sheave. Selecting the correct motor type and capacity is crucial for smooth operation and energy efficiency.
Applicable to geared traction elevators, gearboxes reduce the motor speed and increase torque to drive the traction sheave. Regular inspection and maintenance of gearbox components, such as gears, bearings, and lubricants, are essential to prevent mechanical failure.
Traction sheaves guide the steel ropes that lift and lower the elevator cab. Proper selection of sheave diameter, groove design, and rope quality impacts ride comfort, safety, and long-term durability. Gearless elevators typically require larger sheaves and specialized ropes for high-speed operation.
Braking systems are critical safety components that control the stopping and holding of the elevator cab. This includes electromechanical brakes, safety interlocks, and emergency brakes, all of which must be compatible with both geared and gearless traction machines.
Bearings support the smooth rotation of sheaves and motors, while other safety components—such as buffers, governor systems, and overspeed devices—ensure compliance with international elevator safety standards. Regular inspection and replacement of these parts are essential for maintaining operational safety.
Panda Elevator Parts provides high-quality replacement and upgrade components for both geared and gearless traction elevators. These components are designed to ensure reliable operation, longer service life, and compliance with international elevator safety standards.
By sourcing components from Panda Elevator Parts, maintenance teams and elevator manufacturers can reduce downtime, improve ride quality, and extend the lifespan of both geared and gearless traction systems.
Selecting the right traction elevator system depends on multiple factors, including building height, passenger traffic, speed requirements, budget, and long-term maintenance considerations. Understanding the trade-offs between geared and gearless systems is essential for making informed decisions.
When planning an elevator project or modernization, it is important to source high-quality traction system components that match the selected elevator type. Panda Elevator Parts provides a full range of motors, gearboxes, sheaves, brakes, and safety components compatible with both geared and gearless systems, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Different building types have varying requirements for elevator speed, capacity, and operational efficiency. Choosing the right traction system ensures optimal performance and passenger satisfaction.
In office buildings and shopping centers, passenger traffic can be high during peak hours. Gearless traction elevators are often preferred for their higher speed and smooth ride quality, providing better service and reducing wait times.
For mid to high-rise residential towers, both geared and gearless traction elevators can be used depending on budget and speed requirements. Gearless systems offer quieter operation, which is often preferred in residential environments.
Hospitals require reliable, smooth, and fast elevators to transport patients, staff, and medical equipment. Gearless traction elevators are typically chosen for critical applications, while high-quality components are essential for consistent performance.
In warehouses, factories, and logistics centers, elevators need to handle heavy loads and operate continuously. Geared traction elevators are often suitable due to their durability and lower upfront cost, provided that speed is not the primary concern.
The main difference lies in the drive mechanism: geared elevators use a motor connected to a gearbox to drive the traction sheave, while gearless elevators use a direct-drive motor without a gearbox. This results in differences in speed, maintenance, energy efficiency, and ride quality.
Gearless traction elevators are generally more energy-efficient due to the elimination of gearbox losses and the availability of modern regenerative drives. Geared elevators have slightly higher energy consumption because of mechanical friction in the gearbox.
Geared traction elevators are typically used for low to mid-rise buildings. For high-rise applications, gearless elevators are preferred due to their higher speed and smoother operation.
Consider factors such as building height, passenger traffic, required speed, maintenance capabilities, energy efficiency, and budget. Gearless systems are ideal for high-speed, high-rise applications, while geared systems are cost-effective for mid-rise buildings.
Yes, Panda Elevator Parts provides a comprehensive range of high-quality motors, gearboxes, sheaves, brakes, and safety components compatible with both geared and gearless traction elevators.
Understanding the differences between geared and gearless traction elevators is essential for making informed decisions regarding system selection, maintenance planning, and component sourcing. Geared elevators offer cost-effective solutions for mid-rise buildings, while gearless systems provide superior speed, energy efficiency, and ride comfort for high-rise applications.
By selecting the right traction system and sourcing high-quality components from trusted suppliers like Panda Elevator Parts, elevator manufacturers, maintenance teams, and project engineers can ensure reliable operation, reduce downtime, and extend the service life of their elevator systems.
For more information on Panda's traction system components, including motors, gearboxes, sheaves, and braking systems, please visit our Panda Elevator Parts product catalog or contact our team for personalized guidance.