
Elevator door operators are essential systems responsible for the controlled opening and closing of elevator car doors and landing doors. They directly influence passenger safety, ride comfort, traffic efficiency, and long-term maintenance performance in modern elevator installations.
Unlike simple mechanical door mechanisms, modern elevator door operators integrate electric motors, control units, transmission components, and safety devices to ensure smooth, synchronized, and reliable door movement. These systems are designed to operate under strict international safety regulations while adapting to different building types and usage frequencies.
In commercial buildings, residential complexes, hospitals, and industrial facilities, the performance of the door operator often determines how users perceive elevator quality. Poor door operation can lead to increased downtime, higher maintenance costs, and safety risks.
Because door systems account for a significant portion of elevator faults, choosing a reliable and well-designed door operator is critical for both new installations and modernization projects.
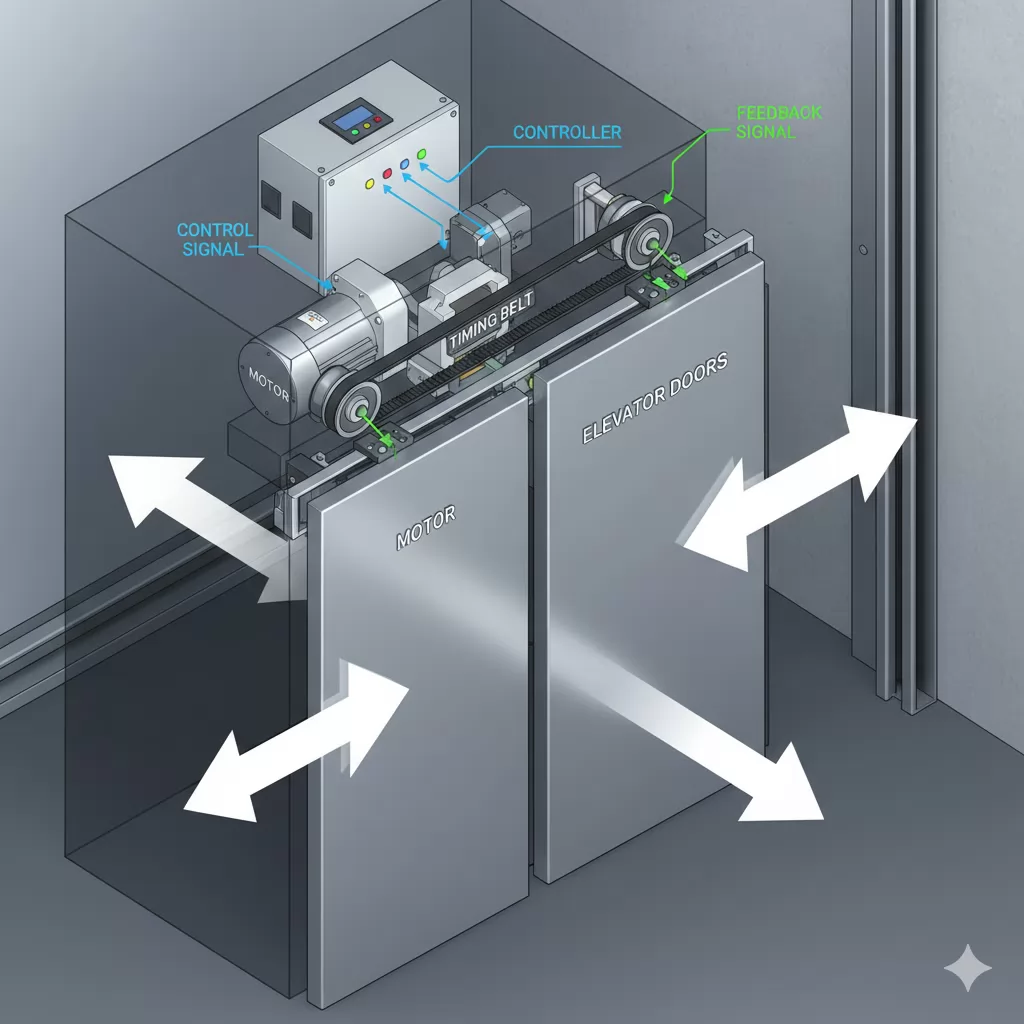
An elevator door operator works by converting electrical control signals into precise mechanical motion that opens and closes the elevator doors in a safe and controlled sequence. The system operates in coordination with the elevator controller, door sensors, and safety circuits to ensure reliable performance at every landing.
When the elevator car arrives at a floor and comes to a complete stop, the main elevator controller sends an open-door command to the door operator. The door operator controller then activates the drive motor, which transmits motion through a belt, gear, or linkage system to move the door panels.
During operation, the door operator continuously monitors door position, speed, and resistance. If abnormal resistance or an obstacle is detected, the system immediately stops or reverses door movement to prevent injury or damage.
Modern elevator door operators rely on closed-loop control systems. Encoders, limit switches, and current sensors provide real-time feedback to the controller, allowing precise regulation of door speed and torque. This feedback-driven control helps reduce mechanical wear, minimize noise, and improve passenger comfort.
Advanced door operators may also feature adaptive control algorithms that adjust door behavior based on usage frequency, door weight, and environmental conditions. This makes them especially suitable for high-traffic commercial buildings and public facilities.
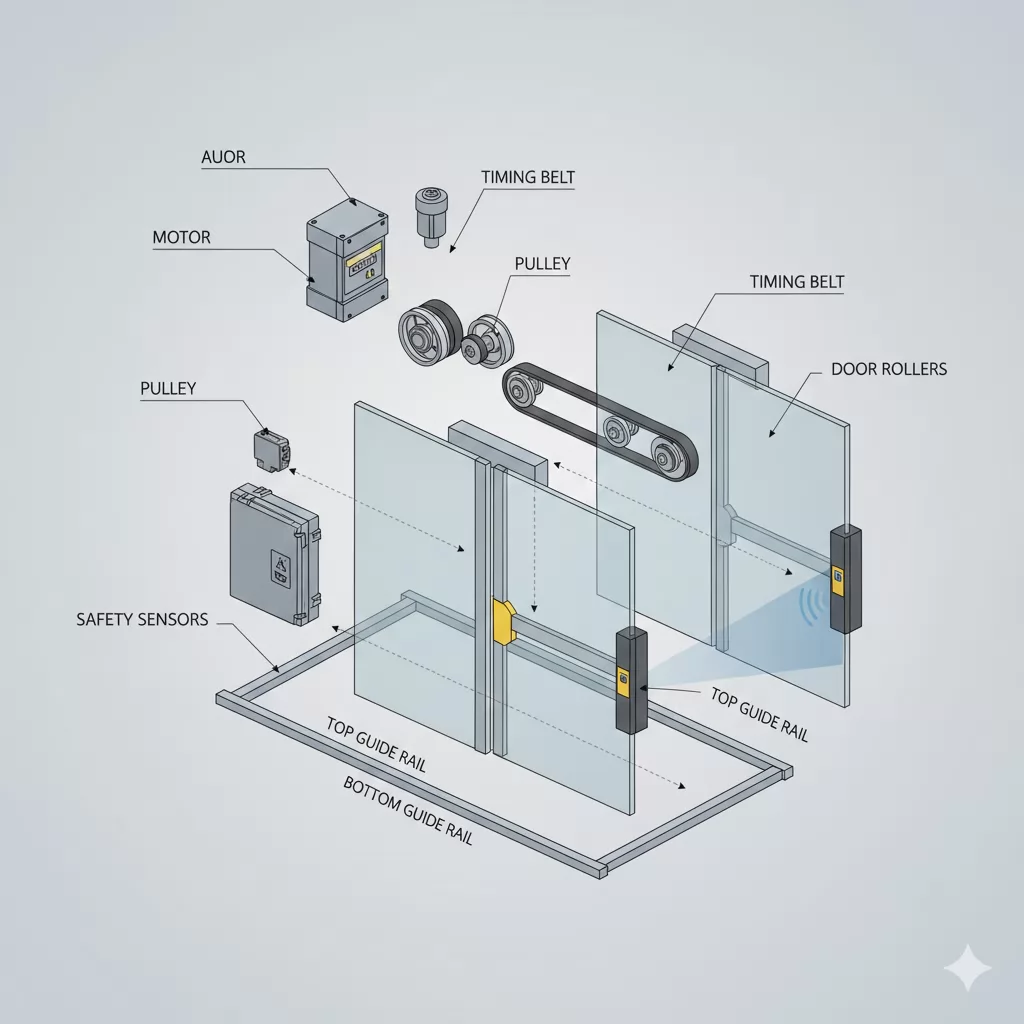
An elevator door operator is composed of several mechanical, electrical, and electronic components that work together to ensure smooth, reliable, and safe door operation. Each component plays a specific role in motion control, safety protection, and system stability.
The motor is the driving force of the elevator door operator. It provides the torque required to open and close the doors at controlled speeds. Modern door operators typically use AC or DC motors designed for high durability, low noise, and precise speed control.
The controller acts as the brain of the door operator system. It receives commands from the main elevator controller and processes feedback signals from sensors to regulate motor speed, torque, and direction.
The transmission system transfers motion from the motor to the door panels. Depending on the design, this may include belts, gears, pulleys, or linkage mechanisms. A well-designed transmission system ensures smooth movement and accurate door positioning.
Door panels move along guide rails with the support of rollers or hangers. These mechanical components must maintain precise alignment to prevent vibration, noise, and uneven wear during operation.
Safety devices are critical for preventing accidents and ensuring compliance with elevator safety standards. These components continuously monitor door movement and detect obstructions or abnormal resistance.
Together, these components form an integrated system that balances performance, safety, and durability. The quality of each component directly impacts the reliability and lifespan of the elevator door operator.

Elevator door operators can be classified based on how the doors open, the number of panels involved, and their application scenarios. Different door operator types are designed to meet specific space constraints, traffic demands, and architectural requirements.
Center-opening door operators move two door panels from the center toward both sides simultaneously. This design provides a wide opening and balanced motion, making it one of the most common configurations in passenger elevators.
Side-opening door operators move one or two door panels to one side. This type is suitable for installations with limited shaft width or specific architectural layouts.
Telescopic door operators use multiple overlapping panels that slide together in the same direction. This design allows for a wider opening in a compact space, making it ideal for locations where shaft width is restricted.
Glass door operators are designed to support transparent or frameless door panels, often used in panoramic elevators. These operators require precise control to handle the weight and balance of glass panels.
Each type of elevator door operator has its own advantages and limitations. The selection should be based on building design, usage frequency, safety requirements, and long-term maintenance considerations.
Elevator door operators are widely used across various types of elevator systems, each with distinct operational requirements and performance expectations. Selecting the appropriate door operator depends on passenger flow, load conditions, safety standards, and the operating environment.
In residential and commercial passenger elevators, door operators must deliver smooth, quiet, and reliable performance. These systems often operate at high frequency and directly affect user comfort and perceived elevator quality.
Hospital elevators require door operators with precise control and enhanced safety features. Wide and fast door opening is critical for transporting beds, wheelchairs, and medical equipment efficiently.
Freight elevators operate under heavier loads and more demanding conditions. Door operators in these systems must be robust, durable, and capable of handling larger and heavier door panels.
Panoramic elevators often feature glass or frameless doors that emphasize aesthetics and visibility. Door operators used in these systems must provide precise movement control to maintain alignment and prevent vibration.
By understanding the application-specific requirements, elevator manufacturers and maintenance companies can select door operators that optimize performance, safety, and long-term operational efficiency.
Different types of elevator door operators are designed to meet specific architectural layouts, traffic demands, and functional requirements. The table below provides a practical comparison to help engineers, elevator manufacturers, and buyers evaluate the most suitable option.
| Door Operator Type | Door Opening Style | Space Requirement | Main Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Center-Opening | Two panels open from the center | Medium | Wide opening, balanced motion, smooth operation | Residential and commercial passenger elevators |
| Side-Opening | One or two panels slide to one side | Low | Simple structure, space-saving design | Small passenger elevators, service elevators |
| Telescopic | Multiple panels slide in the same direction | Very Low | Maximum opening width in limited space | Hospital elevators, modernization projects |
| Glass / Frameless | Transparent or frameless sliding panels | Medium | Aesthetic design, high visibility | Panoramic elevators, shopping malls, hotels |
This comparison highlights how door operator selection should balance space constraints, usage frequency, safety requirements, and visual design. Choosing the right type can significantly improve elevator efficiency and reduce long-term maintenance costs.
An elevator door operator is a system that controls the opening and closing of elevator car doors and landing doors. It includes motors, controllers, transmission mechanisms, and safety sensors to ensure smooth and safe door operation.
The main types include center-opening, side-opening, telescopic, and glass/frameless door operators. Each type is designed for specific space constraints, traffic demands, and aesthetic requirements.
When the elevator arrives at a floor, the controller sends a signal to the door operator, which activates the motor and transmission system. Sensors monitor door position, speed, and resistance to ensure safe and precise movement.
Key factors include door type, building architecture, passenger traffic, safety requirements, motor type, and long-term maintenance needs. Proper selection ensures efficient operation, reduced downtime, and compliance with safety standards.
Yes. Passenger elevators prioritize comfort and smooth motion, hospital elevators require wide and fast door opening, and freight elevators need high-torque, heavy-duty operators for larger doors and higher loads.
Elevator door operators are a vital part of any modern elevator system, impacting safety, passenger comfort, and operational efficiency. Understanding their types, core components, working principles, and application scenarios helps engineers, building owners, and maintenance teams make informed decisions when selecting or upgrading elevator door systems.
Choosing the right door operator not only ensures smooth and reliable operation but also reduces maintenance costs and enhances long-term performance. By considering factors such as building type, traffic volume, door style, and safety requirements, stakeholders can select a solution that meets both functional and aesthetic needs.
For professionals looking to optimize their elevator systems, staying informed about the latest door operator technologies and standards is essential. Reliable door operators are a key investment for safety, efficiency, and user satisfaction.
If you are planning a new installation or modernization project, consult with trusted elevator component suppliers to find a door operator system that aligns with your requirements.